
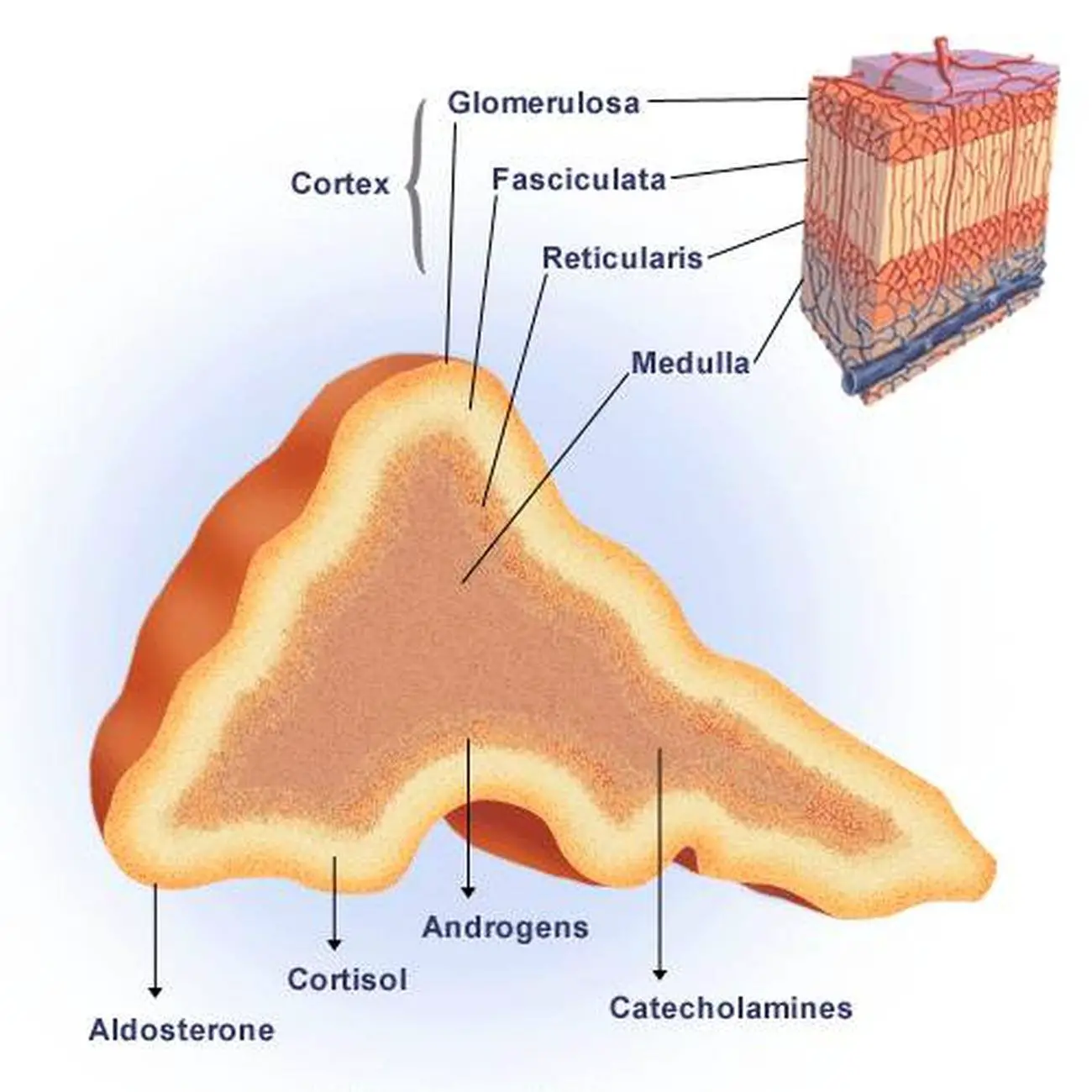
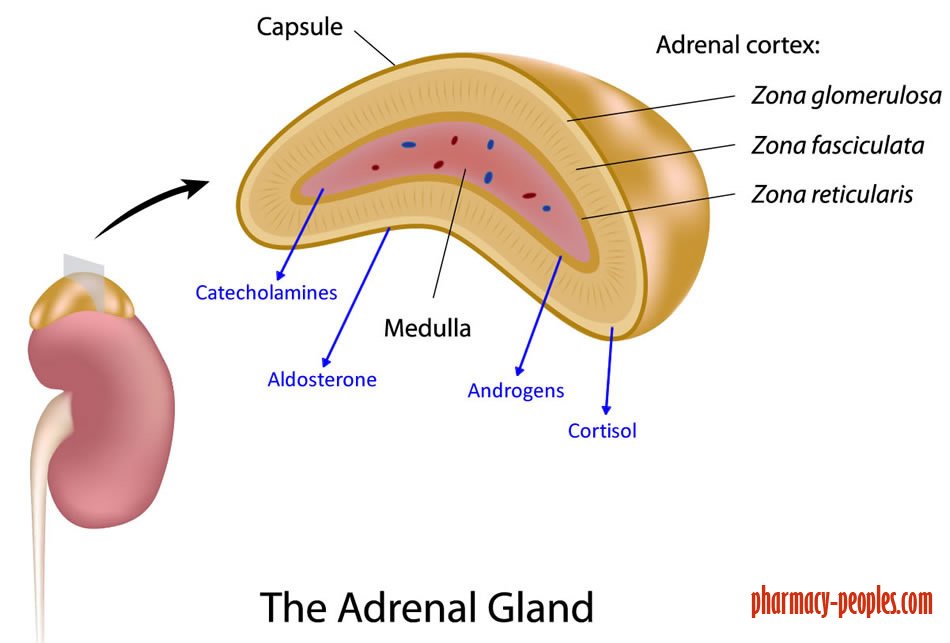
(Micrograph provided by the Regents of University of Michigan Medical School © 2012) The cortex can be subdivided into additional zones, all of which produce different types of hormones. Both adrenal glands sit atop the kidneys and are composed of an outer cortex and an inner medulla, all surrounded by a connective tissue capsule.
If there is no change in the levels of ACTH and cortisol, the etiology is likely to be ectopic.\): Adrenal Glands. If there is a further increase in ACTH and cortisol, the etiology is likely to be a pituitary adenoma. Recall that CRH is released from the hypothalamus to stimulate the pituitary to secrete ACTH.
A CRH-stimulation test can be done in place of the high-dose dexamethasone suppression test. Therefore, there will be no change in cortisol after a high-dose suppression test. Ectopic production of ACTH is not within the axis and will not respond to feedback mechanisms. Therefore, with a high-dose suppression test, the production of ACTH will decrease leading to a decrease in cortisol. A pituitary adenoma will still respond to the hypothalamic-pituitary axis however, it needs more feedback to do so. A high-dose, typically 8 mg, dexamethasone-suppression test is done. If the secondary hypercortisolism is suspected, testing must be done to differentiate between a pituitary cause or an ectopic cause. Cushing syndrome is associated with ectopic ACTH production. Normal feedback loop mechanisms do not control the production of the hormone. Benign or malignant tumors secrete hormones. Diseases associated with the adrenals include Addison and Cushing.Įctopic secretion refers to the production of a hormone outside of its normal physiology mechanism. The adrenal can also be hypofunctioning or hyperfunctioning. It is a pituitary infarct after massive blood loss during childbirth. Sheehan syndrome is a less common cause of pituitary insufficiency. It can also be caused by pituitary apoplexy, a sudden hemorrhage into a pituitary tumor causing sudden loss of ACTH. Pituitary insufficiency is usually the result of an adenoma that destroys the gland. The pituitary can be hypofunctioning or hyperfunctioning, leading to either a decrease or increase, respectively, in ACTH. Issues can be with the pituitary, adrenals, or ectopic secretion.

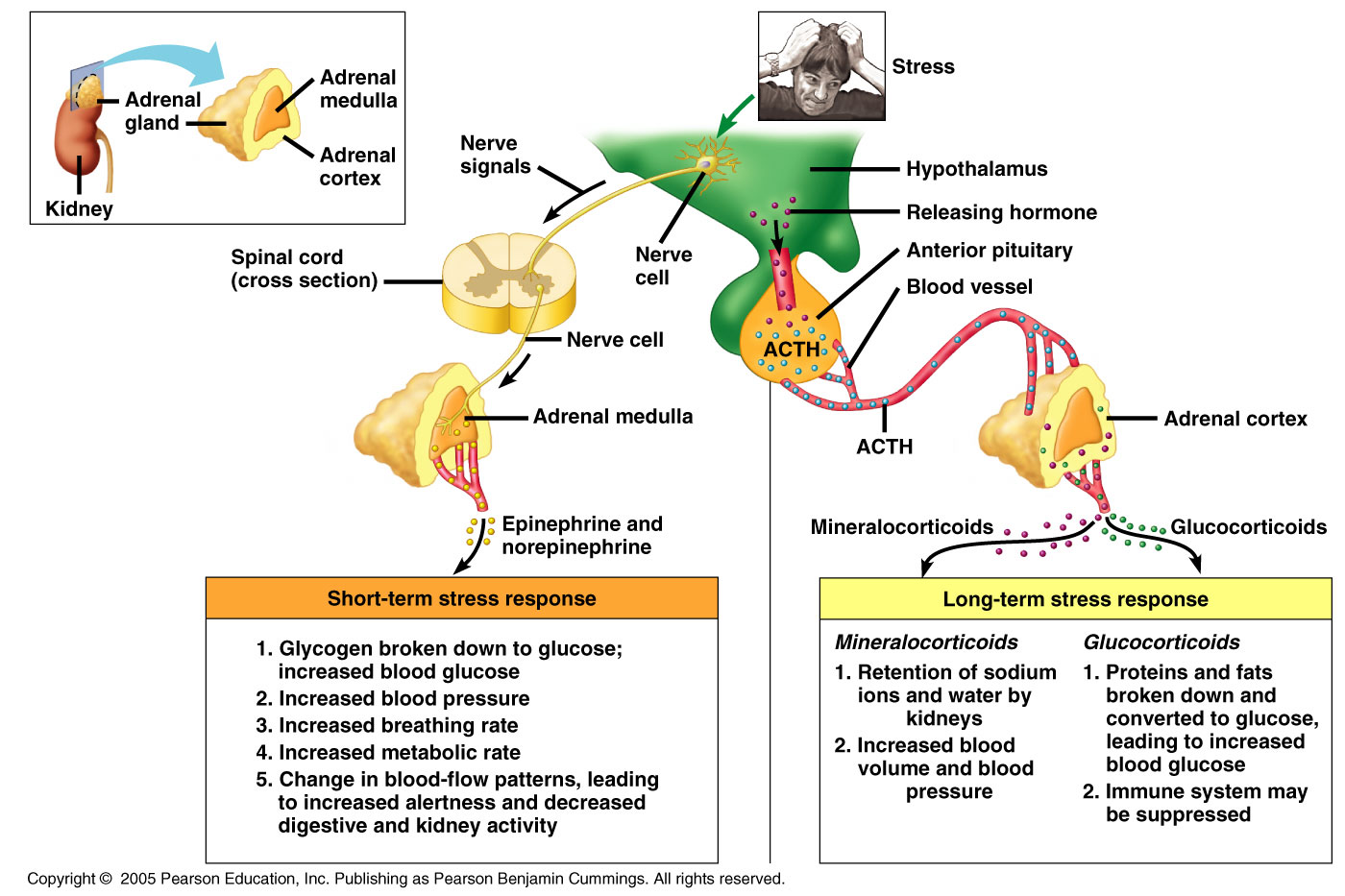
Pathophysiology associated with ACTH can stem from 3 different mechanisms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
